Abnormal liver enzymes: To steroid or not to steroid?
What is Drug-induced AIH-like liver injury and how does it present?
- Drug-induced liver injury can be associated with autoimmune-like features and may account for 9-12% of cases with classical features of AIH
- Key clinical features in drug-induced AIH-like liver injury include right upper quadrant pain, hypersensitivity manifestations including fever, rash, arthralgias, eosinophilia and positive autoantibodies (antibodies to nuclear antigen [ANA], smooth muscle [SMA] and soluble liver antigen [SLA])
How is a diagnosis of drug-induced liver injury made?
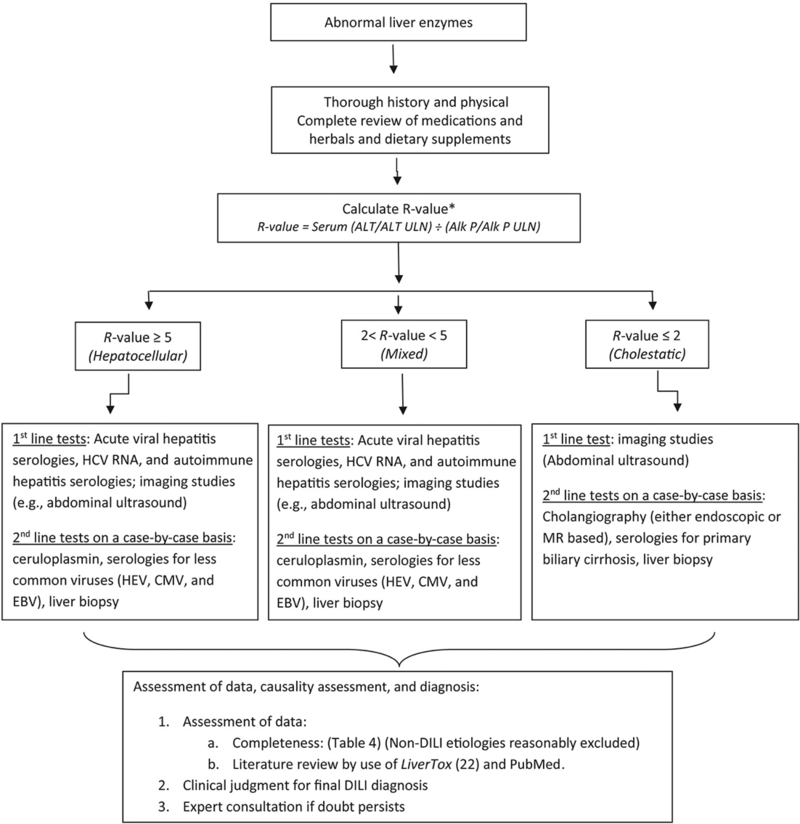
Obtaining an accurate clinical history is key. In addition, the American College of Gastroenterology set forth a helpful diagnostic algorithm to evaluate for suspected idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury (Figure 1).
Figure 1- An algorithm to evaluate for suspected idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury
Taken from: Chalasani, N., et al., ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Am J Gastroenterol, 2021. 116(5): p. 878-898.
Drug-induced AIH-like liver injury – Medication history
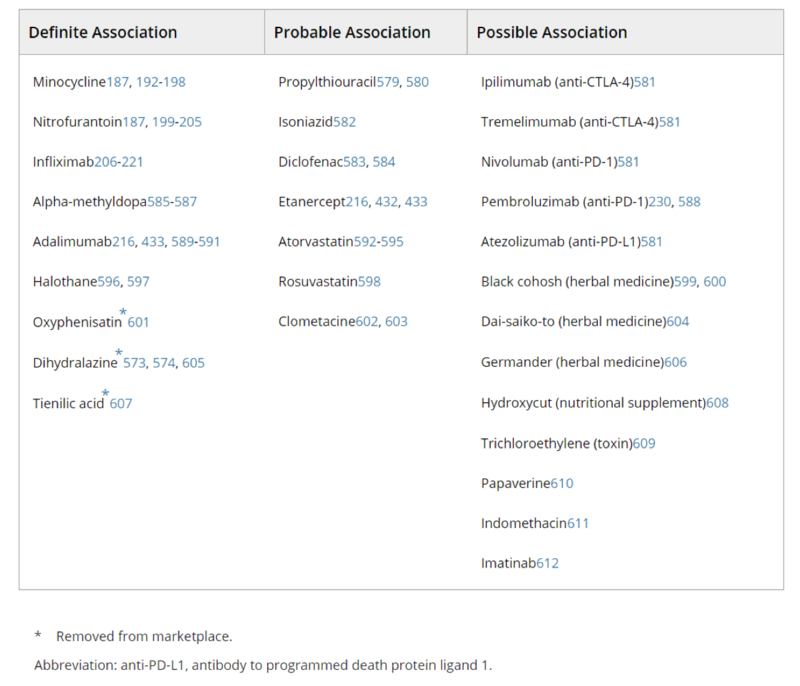
- Nitrofurantoin, minocycline, hydralazine, methyldopa and infliximab are the most common drugs shown to have a definite association with drug-induced AIH-like liver injury
- The latency period from drug exposure to disease onset in drug-induced AIH-like liver injury can be as short as 1 week to as long as over 12 months, though it is rare to see the presence of autoantibodies prior to 2 months after drug exposure
- Other drugs associated with liver injuries resembling AIH are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Drugs Associated with Liver Injuries Resembling AIH
Taken from: Mack, C., et al., Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults and Children: 2019 Practice Guidance and Guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology, 2020. 72(2): p. 671-722.
Figure 2: Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis
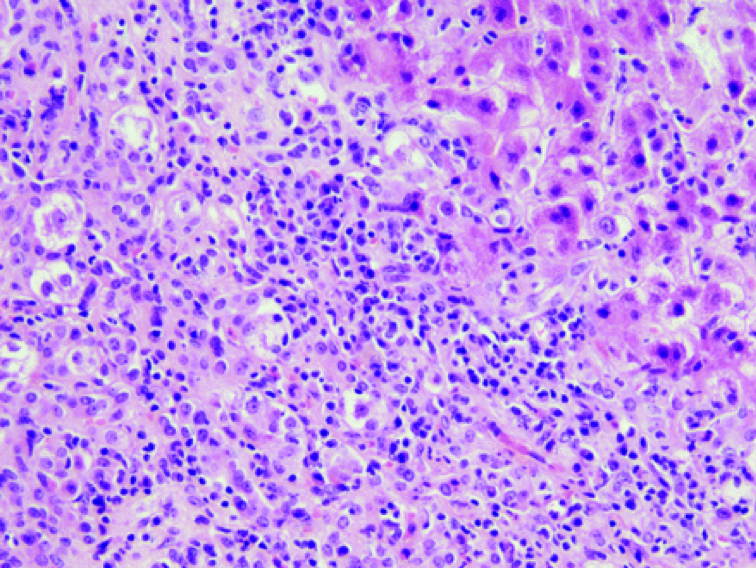
Taken from: Ramachandran, R., and Sakar, S., Histological patterns in drug-induced liver injury. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 2009. 62: p. 481-492.
Drug-induced AIH-like liver injury – Liver biopsy
- Liver biopsy is warranted if there is diagnostic uncertainty, if labs indicate severe injury, or if glucocorticoid therapy is being considered
- Liver biopsies in drug-induced AIH-like liver injury usually show features that are typical of autoimmune hepatitis such as interface hepatitis and lymphoplasmocytic infiltrates
- The absence of advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis on biopsy may help to differentiate drug-induced AIH-like liver injury from classical AIH
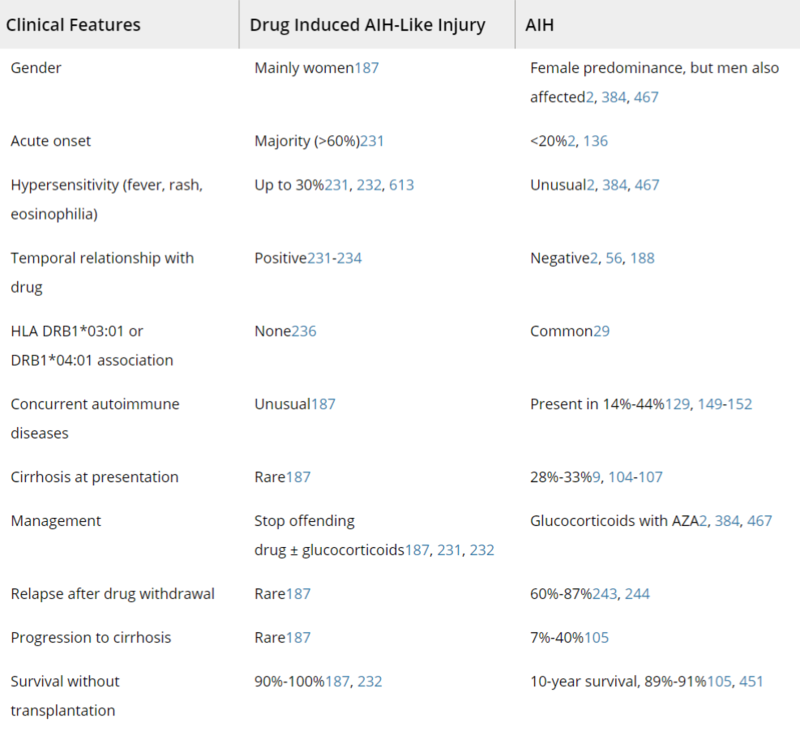
- The 2019 AASLD Practice Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults and Children highlights features of drug-induced AIH-like liver injury vs. AIH (Table 2)
Table 2: Features of drug-induced AIH-like injury and AIH
Taken from: Mack, C., et al., Diagnosis and Management of Autoimmune Hepatitis in Adults and Children: 2019 Practice Guidance and Guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology, 2020. 72(2): p. 671-722.
Drug-induced AIH like liver injury -- Treatment
- The mainstay of therapy for drug-induced AIH-like liver injury is withdrawal of the culprit drug with close monitoring until complete and sustained resolution of clinical and laboratory findings
- Corticosteroid therapy is appropriate if there is no evidence of recovery within weeks of stopping the medication, if labs continue to worsen, or if there is any evidence of hepatic failure such as prolongation of PT-INR, progressive jaundice, or new hepatic encephalopathy or ascites
- The outcome of drug-induced AIH-like liver injury is excellent and many patients respond to corticosteroid therapy
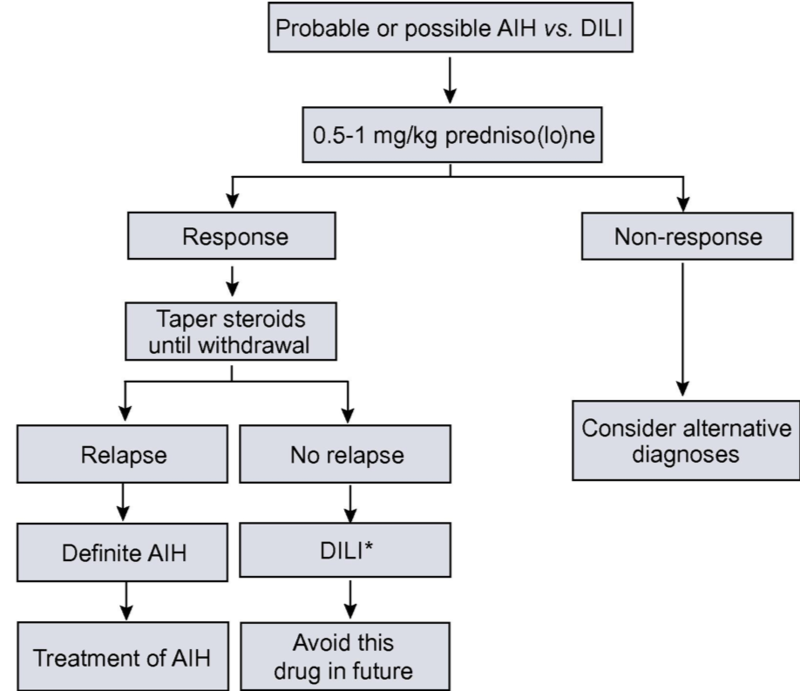
- Patients with suspected drug-induced AIH-like liver injury should be closely monitored for at least 6 months after corticosteroids have been withdrawn to confirm full recovery and absence of relapse, which would suggest underlying spontaneous AIH. The presumptive drug culprit should be avoided to avoid triggering relapse. (Figure 3)
Figure 3: Suggested treatment algorithm for autoimmune hepatitis vs. drug-induced autoimmune-like liver injury
Taken from: EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol, 2015. 63(4): p. 971-1004.